is a collaborative project to deliver traditional API services to smart contract platforms in a decentralized and trust-minimized way. It is governed by a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), namely the .
For more info about API3, check out its .
An is a first-party oracle that pushes off-chain API data to your on-chain contract. Airnode lets API providers easily run their own oracle nodes. That way, they can provide data to any on-chain app that's interested in their services, all without an intermediary.
are continuously updated streams of off-chain data, such as the latest cryptocurrency, stock and commodity prices. They can power various decentralized applications such as DeFi lending, synthetic assets, stablecoins, derivatives, NFTs, and more.
The data feeds are continuously updated by using signed data. App owners can read the on-chain value of any dAPI in real-time. Due to being composed of first-party data feeds, dAPIs offer security, transparency, cost-efficiency, and scalability in a turn-key package.
Apart from relying on deviation threshold and heartbeat configuration updates, unlike traditional data feeds, enables apps using dAPIs to auction off the right to update the data feeds to searcher bots. Searcher bots can bid for price updates through the OEV Network to update the data feeds. All the OEV proceeds go back to the app.
The enables users to connect to a dAPI and access the associated data feed services. to learn more about how dAPIs work.
The lets users access dAPIs on both the and .
The currently supported configurations for dAPIs are:
0.25%
24 hours
0.5%
24 hours
1%
24 hours
5%
24 hours
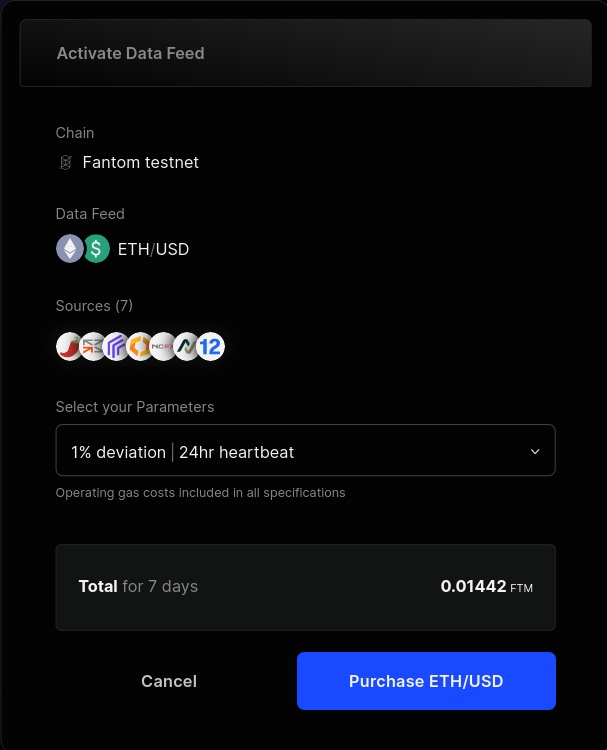
If a dAPI is already activated, make sure to check the expiration date and update the parameters. You can update the parameters and extend the subscription by purchasing a new configuration.
After selecting the dAPI and the configuration, you will be presented with an option to purchase the dAPI and activate it. Make sure to check the time and amount of the subscription. If everything looks good, click on Purchase.
You can then connect your wallet and confirm the transaction. Once it's confirmed, you will be able to see the updated configuration for the dAPI.
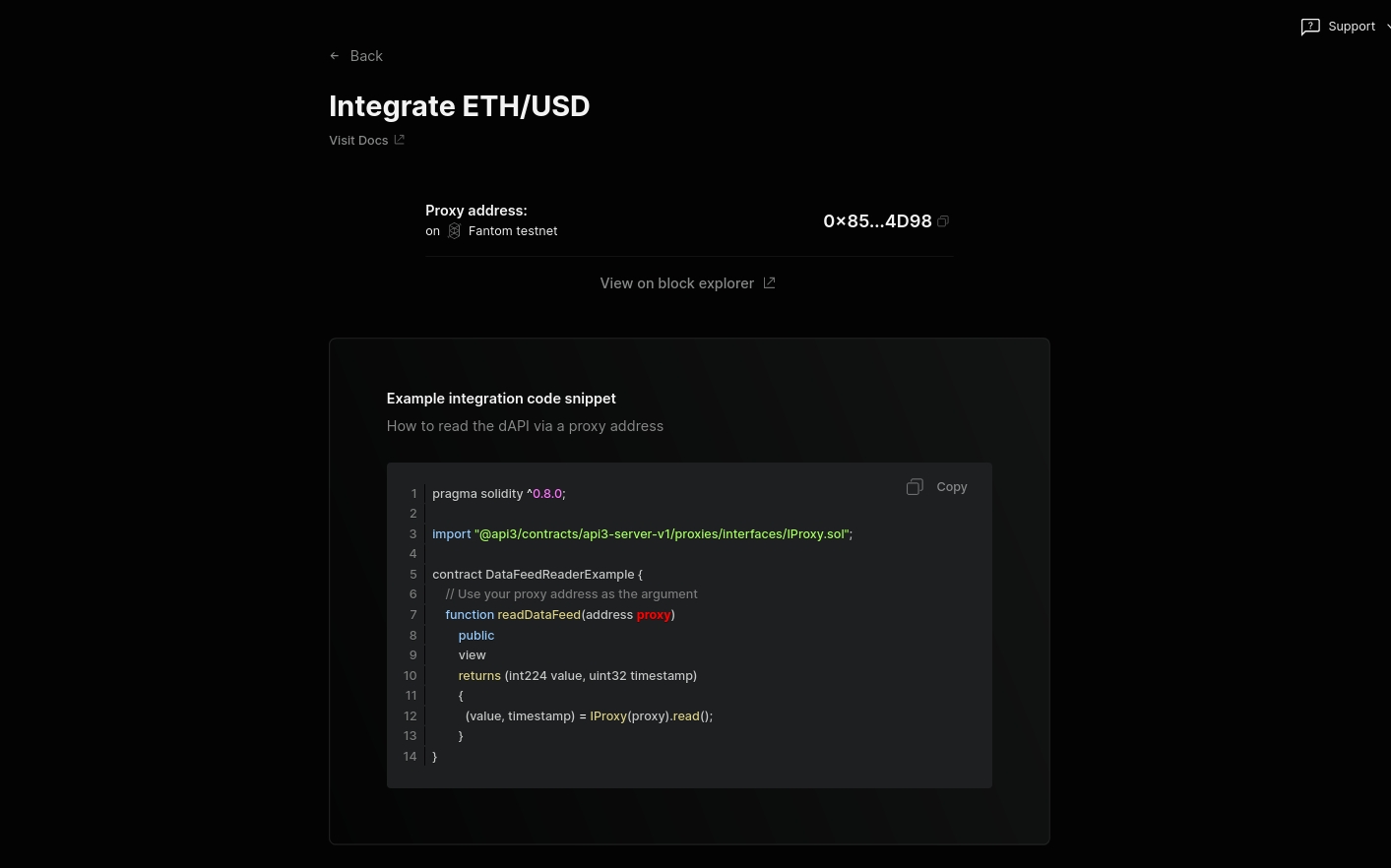
Once you are done configuring and activating the dAPI, you can now integrate it. To do so, click on the Integrate button on the dAPI details page.
You can now see the deployed proxy contract address. You can now use this to read from the configured dAPI.
Here's an example of a basic contract that reads from a dAPI:
setProxyAddress() is used to set the address of the dAPI Proxy Contract.
readDataFeed() is a view function that returns the latest price of the set dAPI.
Here are some additional developer resources:
The provides a list of all the dAPIs available across multiple chains, including testnets. You can filter the list by mainnet or testnet chains. After selecting the chain, you can now search for a specific dAPI by name. Once selected, you will land on the details page (eg ETH/USD on the Opera Testnet) where you can find more information about the dAPI.
You can read more about dAPIs .